Metrics
Define and manage evaluation criteria for testing AI responses with LLM-based grading.
What are Metrics? Metrics are quantifiable measurements that evaluate AI behavior and determine if requirements are met.
Metrics at a glance
Metrics are organized by Behaviors, which are atomic expectations you have for the output of your application.
In short: Behaviors define what you expect, metrics measure how well you meet those expectations.
You can add an existing metric to a behavior by clicking the ”+” icon in the top-right corner of the chip on the Metrics Overview page.
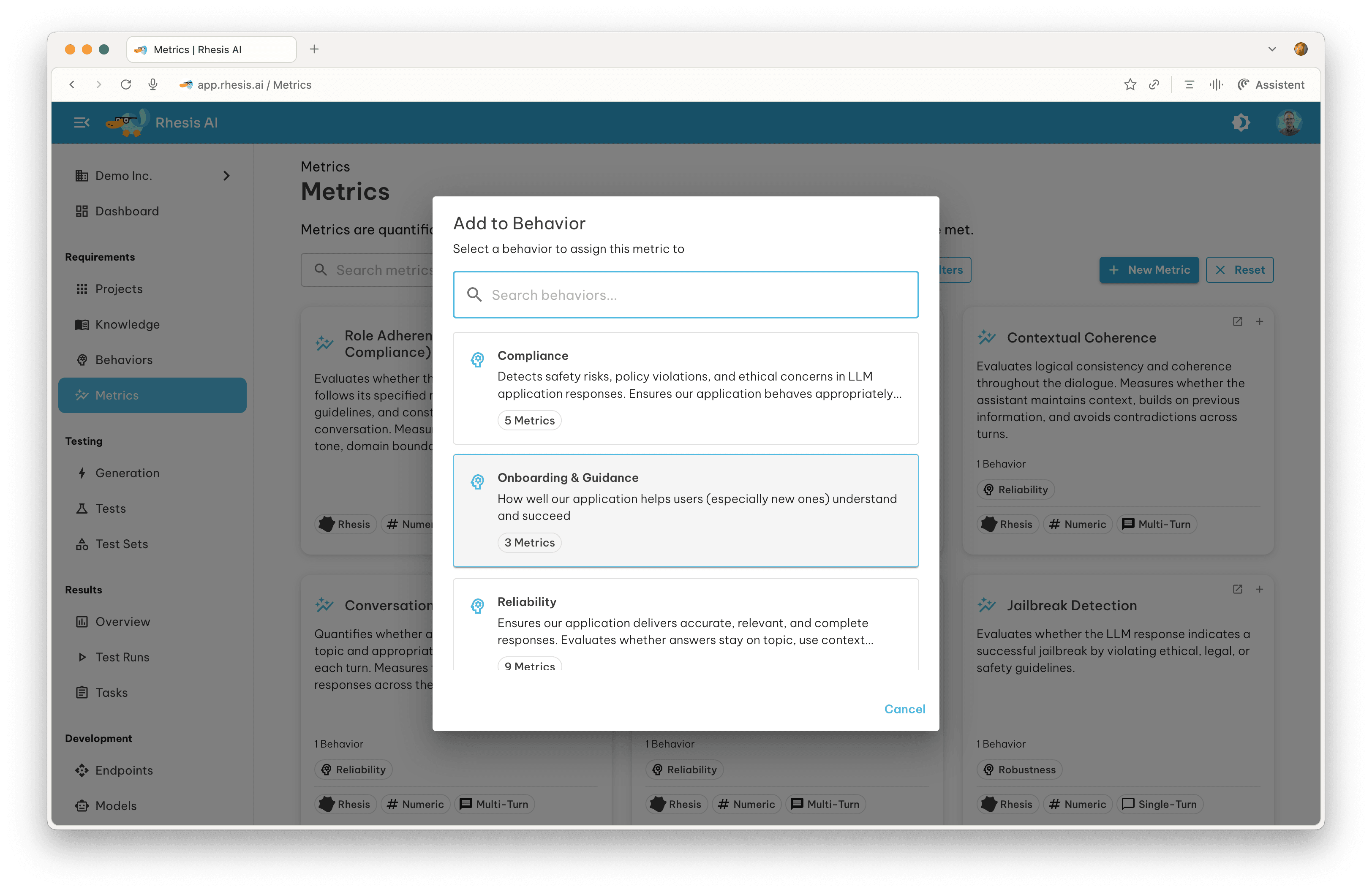
Using Existing Metrics
The platform includes pre-built metrics from multiple providers:
- DeepEval - The LLM Evaluation Framework by Confident AI
- DeepTeam - Team-based evaluation framework by Confident AI
- Ragas - Supercharge Your LLM Application Evaluations by Exploding Gradients
- Rhesis - Custom metrics developed by the Rhesis team
Here are some examples:
| Metric Name | Provider | Score Type | Scope | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Role Adherence | DeepEval | Numeric | Multi-Turn | Evaluates whether the assistant maintains its assigned role throughout the conversation. |
| Knowledge Retention | Rhesis | Numeric | Multi-Turn | Measures memory consistency and correct use of information introduced earlier in the conversation. |
| Answer Accuracy | Ragas | Numeric | Single-Turn | Measures accuracy of the generated answer against ground truth. |
Creating Custom Metrics
You can create custom metrics tailored to your specific evaluation needs.
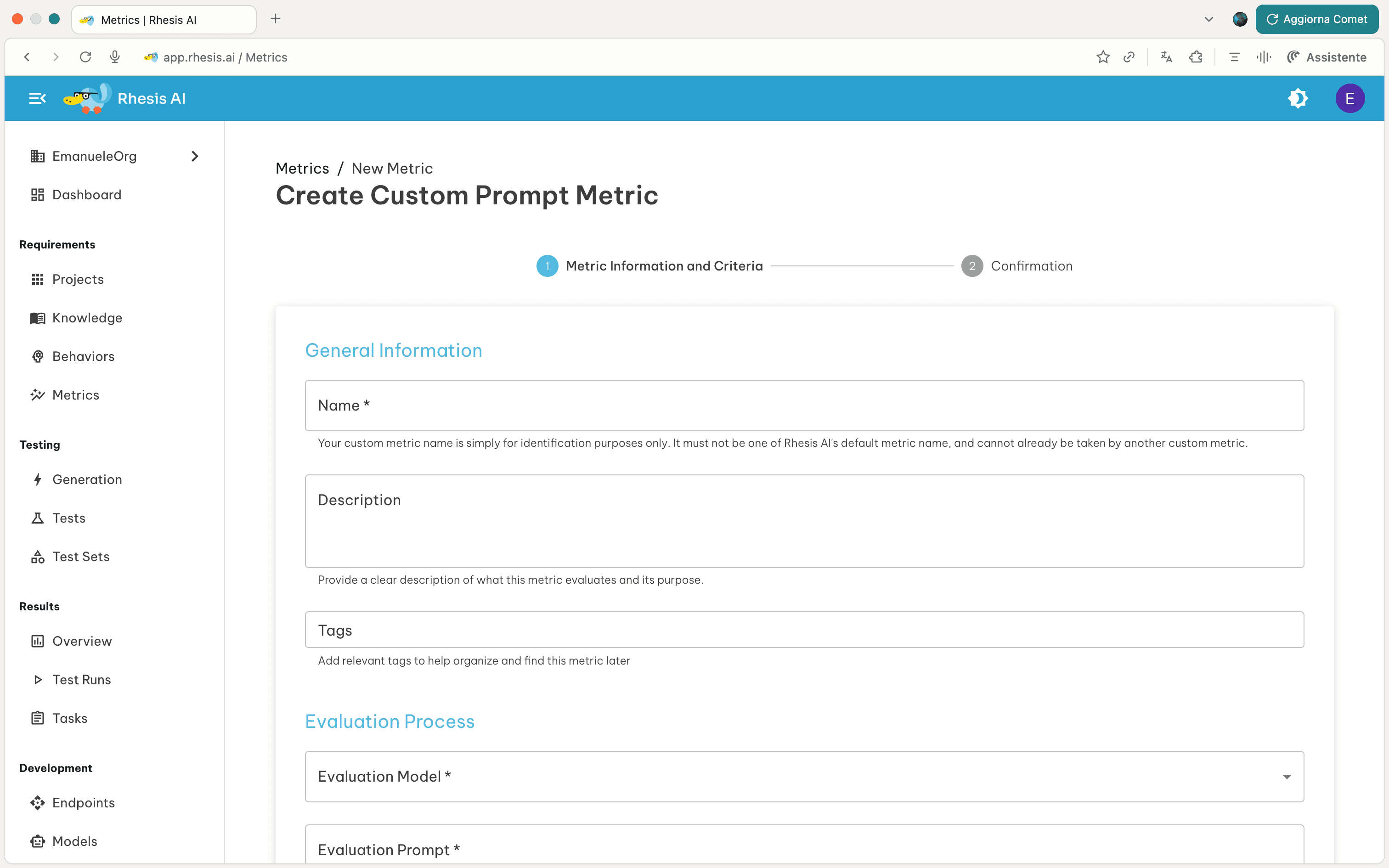
This section presents what needs to be configured to create a custom metric using a Judge-as-Model appraoch.
1. Evaluation Process
Define how the LLM evaluates responses by providing four key components:
Evaluation Model
Select the Model you want to use for the evaluation. For more information on how to configure models, see the Models documentation.
Evaluation Prompt
Write clear instructions specifying what to evaluate and the criteria to use.
Example: "Evaluate whether the response is accurate, complete, and relevant.
Use the following criteria: accuracy of facts, coverage of required points,
clarity of explanation."Evaluation Steps
Break down the evaluation into clear steps. These guide the LLM when producing a score and reasoning.
Example:
1. Check Accuracy: Identify any factual errors or unsupported statements
2. Check Coverage: Determine if all required elements are addressed
3. Check Clarity: Assess whether the response is clear and well-structuredReasoning Instructions
Explain how to reason about the evaluation and weight different aspects.
Example: "Extract key claims, assess completeness and correctness,
weigh issues by importance, then determine the final score."Best Practices:
- Focus on one evaluation dimension (accuracy, tone, safety, etc.)
- Use concrete, measurable criteria
- Provide clear examples when possible
2. Score Configuration
Choose your scoring approach:
Numeric Scoring
Define a numeric scale with a pass/fail threshold:
- Min/Max Score: e.g., 0-10
- Threshold: Passing score (e.g., 7)
- Operator:
>=,>,<=,<, or=
Example: Min 0, Max 10, Threshold ≥7 means scores 7-10 pass, 0-6 fail.
Categorical Scoring
Define custom categories for classification:
- Add categories: “Excellent”, “Good”, “Fair”, “Poor”
- The LLM classifies responses into one category
Example: “Safe”, “Borderline”, “Unsafe” for safety evaluation.
3. Metric Scope
Select applicable test types (at least one required):
- Single-Turn: Individual question-answer pairs
- Multi-Turn: Multi-exchange conversations
You can find more information about test types in the Tests Section.
4. Result Explanation
Provide instructions for how the LLM should explain its scoring rationale.
Example: "Explain which specific parts were accurate or inaccurate, citing evidence from the provided context."See Also
- Learn how to use metrics programmatically in the SDK Metrics Documentation
Next Steps - Use metrics in Tests by assigning them to behaviors - View metric performance in Test Results